Manufacturing engineers are absolutely essential in making sure goods are built sustainably and effectively in the highly industrialized society of today. From automotive to aerospace, these experts operate in several sectors and significantly boost the global economy. We examine in this paper the several aspects of manufacturing engineering, its difficulties, developments, and the knowledge required for success.
1. Manufacturing Engineering Overview
A specialized field of engineering, manufacturing engineering is concerned in designing, assessing, and enhancing production techniques. It entails using innovative technology to satisfy market needs, improving product quality, and maximizing manufacturing efficiency. Manufacturing engineers’ work is vital in sectors ranging from consumer electronics to healthcare where accuracy and output are critical.
2. Important Roles and Responsibilities for a Manufacturing Engineer
Though mostly focused on process optimization and quality control, manufacturing engineers have a broad range of tasks. They guarantee maximum performance and low waste in manufacturing of items, so ensuring their efficiency. Among their major responsibilities are:
Planning and planning manufacturing processes; supervising production activities; applying process enhancements and quality assurance procedures; working with design and development teams to maximise manufacturing product designs;
3. Critical Competencies for a Manufacturing Engineer in Demand
A effective manufacturing engineer calls for a varied skill set. Among the most important ones are:
Critical thinking and problem-solving skills
Mastery of sophisticated manufacturing technologies like CAD/CAM systems
Particularly in cross-functional teams, strong communication and teamwork abilities; also, aptitude for lifelong learning helps one to remain current with industry developments.
4. Learning Routines to Pursue Manufacturing Engineer Employment
Usually needing at least a bachelor’s degree in mechanical engineering, industrial engineering, or a similar profession, manufacturing engineers Whether through internships or hands-on training, practical experience is also absolutely vital. Further improving a manufacturing engineer’s employment possibilities is ongoing education and certifications in lean manufacturing or Six Sigma.
5. Typical Employment Environment and Job Locations
Depending on their field of expertise, manufacturing engineers operate in many surroundings. Among the most often occurring environments are:
Many engineers labor on the manufacturing floor of factories and manufacturing plants, making sure production lines and machinery are running as they should. As problems surface, they might track manufacturing, supervise maintenance, and troubleshoot problems.
Engineers sometimes spend their time between the manufacturing floor and office settings, where they plan and design manufacturing processes or work on product development. Another regular workplace where engineers concentrate on creativity and process enhancement is R&D facilities.
Some manufacturing engineers go to several sites to supervise the deployment of new systems, monitor production processes, or handle particular quality control related concerns.
Typical Difficulties Manufacturing Engineers Face
Like many occupations, manufacturing engineers have certain difficulties that they must properly negotiate to be successful in their roles:
Manufacturing engineers have to strike a compromise between keeping great product quality and optimizing production speed.
Engineers have to constantly upgrade their knowledge and abilities given fast developments in automation, artificial intelligence, and other technologies.
Managing Resource Constraints and Budgets: Cost control is a big issue in manufacturing, hence engineers have to make sure that projects are finished within budget while keeping good standards.
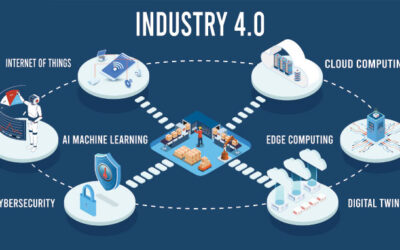
7. Manufacturing Engineer Influence on Industry 4.0
Manufacturing engineers are leading the way as Industry 4.0 transforms the sector. They are quite important in:
Engineers create procedures including robotics to improve accuracy, lower labor costs, and simplify manufacturing.
Manufacturing engineers are progressively using artificial intelligence and data analysis to forecast maintenance needs, maximize production schedules, and enhance quality control.
Engineers are creating greener production techniques including lowering waste and energy usage as growing environmental effect worries them.
8. Manufacturing Engineering: Prospective Career Growth
Manufacturing engineering presents strong chances for career development with chances for advancement into leadership or specialized roles:
Experienced engineers sometimes land in supervisory or managerial roles, supervising bigger teams and complete manufacturing sites.
Engineers can concentrate in increasingly sought-after fields as robotics, additive manufacturing (3D printing), or nanotechnology, advanced manufacturing fields.
From consumer products to healthcare, manufacturing engineers are sought for in many different sectors; many of these positions provide chances to work internationally.
9. Manufacturing Engineer Salary and Employment Forecast
Manufacturing engineers are still in great demand, and their pay reflects their significance in this field:
Manufacturing engineers in the United States make, on average, between $70,000 and $100,000 yearly; in sectors like aerospace and defense, their pay vary.
Growing demand for competent manufacturing engineers results from the introduction of new technologies and increasing attention on sustainable manufacture.
Industries having the Most Manufacturing Engineer Employment: Important sectors using manufacturing engineers are consumer electronics, automobiles, aerospace, and pharmaceuticals.
10. Case Studies of Effective Manufacturing Engineering Efforts
Effective initiatives show the influence manufacturing engineers may have on sectors of business:
Lean manufacturing ideas let engineers help to lower costs and improve efficiency by helping to simplify production and cut waste in the automotive sector.
Using 3D printing to produce smaller, stronger parts at a reduced cost allowed engineers to completely transform aerospace manufacturing.
Engineers brought robots and automation to consumer electronics manufacture, therefore substantially lowering production time and raising output quality.
11. Manufacturing Engineering Technical Innovations
Technology developments are always changing production engineering:
Using additive manufacturing, manufacturing engineers design intricate pieces that would be challenging to produce using conventional techniques and cut material waste.
Using digital twins—virtual replicas of physical assets—engineers may track and maximize production in real-time, including in smart factories.
Engineers are progressively using new materials and nanotechnology to create goods that are stronger, lighter, and more durable.
12. How Product Development Benefits from Manufacturing Engineer Contributions
Product development depends much on manufacturing engineers since they guarantee that designs are production-oriented and hence optimized:
Engineers supervise the development of prototypes and carry testing to guarantee that goods satisfy criteria and can be produced effectively.
Manufacturing engineers make sure that small batch items may be scaled up for mass production while preserving quality and economy of cost.
13. Manufacturing Engineering Future Trends
Manufacturing engineering has a bright future where numerous themes are likely to affect the sector:
As automation gets more sophisticated, we should expect to see completely automated manufacturing with little human interaction.
The Internet of Things (IoT) will let production engineers link equipment and systems, therefore enhancing efficiency and allowing predictive maintenance.
Engineers will keep spearheading initiatives toward more sustainable production, including the creation of circular manufacturing models whereby goods are made to be recycled or reused.
14. Answers Regarding Manufacturing Engineers
What usually constitute the responsibilities of a manufacturing engineer?
Design, improvement, and supervision of production processes are responsibilities of manufacturing engineers, therefore guaranteeing quality and efficiency.
Which abilities will help one succeed in manufacturing engineering?
Important abilities are good communication and teamwork, technical knowledge in manufacturing technology, and problem-solving capacity.
In what ways might manufacturing engineers be different from other engineers?
While other kinds of engineers might concentrate on design, research, or other facets of product creation, manufacturing engineers concentrate mostly on production procedures.
Which businesses use manufacturing engineers?
Among the several sectors they operate in, manufacturing engineers find work in automotive, aerospace, electronics, and pharmaceuticals.
Which technology do manufacturers employ?
They regularly apply robots, CAD/CAM tools, automation systems, and data analysis tools driven by artificial intelligence.
How may manufacturers help to promote sustainability?
Designing methods that cut waste, lower energy usage, and enhance the general environmental impact of manufacturing, manufacturing engineers create
In the modern world, manufacturing engineers play a crucial part. Driving developments in efficiency, quality, and sustainability, manufacturing engineers are indispensable in contemporary industry. From consumer electronics to aerospace, their capacity to embrace new technology and spearhead process changes makes them great assets to many different sectors.