Rethinking Energy Consumption
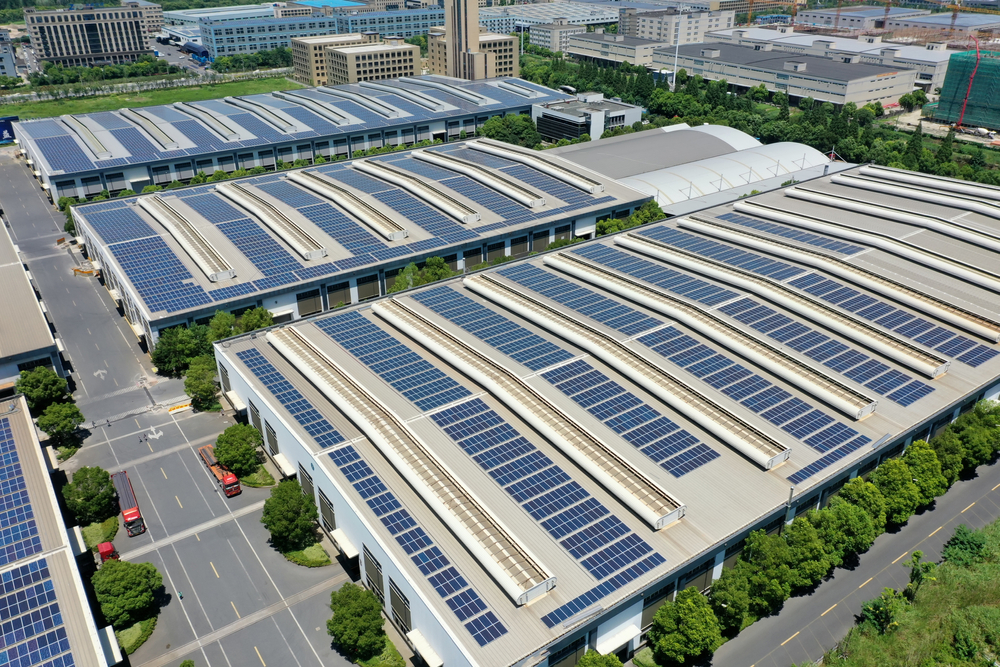
One of the pillars of sustainability is energy efficiency. Manufacturing plants are notoriously energy-intensive, but engineers are now exploiting alternative energy sources and optimizing operations to reduce consumption. By embracing renewable energy, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, manufacturing plants can dramatically lower their carbon footprint. For example, installing solar panels on the roof of a plant can offset energy requirements, whilst on-site wind turbines can supplement the power supply. Manufacturing engineers should also consider conducting regular energy audits to identify areas of energy wastage and inefficiency. Implementing changes based on audit findings, such as optimizing HVAC systems, can lead to significant energy savings.
Circular Economy and Waste Reduction
The traditional linear economy, which follows the “take, make, dispose” model, is not sustainable. The circular economy, on the other hand, emphasizes on resource optimization through recycling, reusing, and reducing waste. Manufacturing engineers should look to integrate this model into their processes by finding innovative ways to reduce waste and reuse materials. For instance, engineers could develop closed-loop systems for water and materials, ensuring that waste is minimized and that any by-products are fed back into the production process. Additionally, fostering relationships with recycling facilities to repurpose waste materials can lead to new revenue streams and reduced environmental impact.
Sustainable Supply Chain Management
Manufacturing processes are just one part of the larger ecosystem. Sustainable manufacturing also involves considering the environmental impact of the supply chain. Engineers can work in tandem with procurement teams to ensure that materials are sourced responsibly and that suppliers uphold sustainable practices. By prioritizing suppliers that hold certifications such as ISO 14001, manufacturing plants can ensure that the raw materials used in their processes are aligned with sustainability goals.
Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
Technological advancements have ushered in an array of possibilities for sustainable manufacturing. Additive manufacturing, for instance, can reduce material waste significantly by using only the necessary materials for production. Digital twin technology allows engineers to create virtual models of their manufacturing processes and optimize them for efficiency and reduced waste. Furthermore, automation and robotics can streamline processes to use resources more efficiently. Investing in these technologies not only boosts sustainability but also enhances productivity and competitiveness.
Employee Training and Culture Shift
Sustainability is not solely about technologies and systems; it’s also about people. A truly sustainable manufacturing plant requires a cultural shift and employee buy-in. Manufacturing engineers should lead by example and advocate for sustainable practices. Training programs can be developed to educate employees on sustainability and its long-term benefits, and to train them in new, greener technologies and practices. By encouraging an ethos of sustainability throughout the organization, manufacturing engineers can foster a culture that is conscious of its environmental impact and continuously strives for improvement.
Localized Production and Distribution
The concept of localized production, often referred to as “reshoring,” involves bringing manufacturing processes closer to the consumer base. This reduces the carbon emissions associated with transporting goods over long distances. With the advent of advanced manufacturing technologies, such as 3D printing, it’s becoming increasingly viable to produce goods locally without incurring exorbitant costs.
Measuring Success
It’s essential to set measurable sustainability goals and continually assess performance against these benchmarks. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as energy consumption, water usage, and waste generation should be monitored regularly. This not only helps in ensuring compliance with regulations but also assists in identifying areas for improvement.
A Multifaceted approach
The transition to sustainable manufacturing requires a multifaceted approach that integrates technology, process optimization, and a shift in culture. As custodians of the manufacturing process, engineers play a pivotal role in driving this change. Through sustainable practices, manufacturing plants can not only reduce their environmental footprint but also unlock new efficiencies and opportunities that ensure long-term viability in an ever-evolving marketplace.